E Waste Recycling and Management, Electronic Scrap Buyers, Dealers, Computer E-Waste Recycling
All kinds of scrap materials such as E-Waste, Metal Scraps Copper, Aluminium, Brass, Steel etc.
All kinds of scrap materials such as E-Waste, Metal Scraps Copper, Aluminium, Brass, Steel etc.
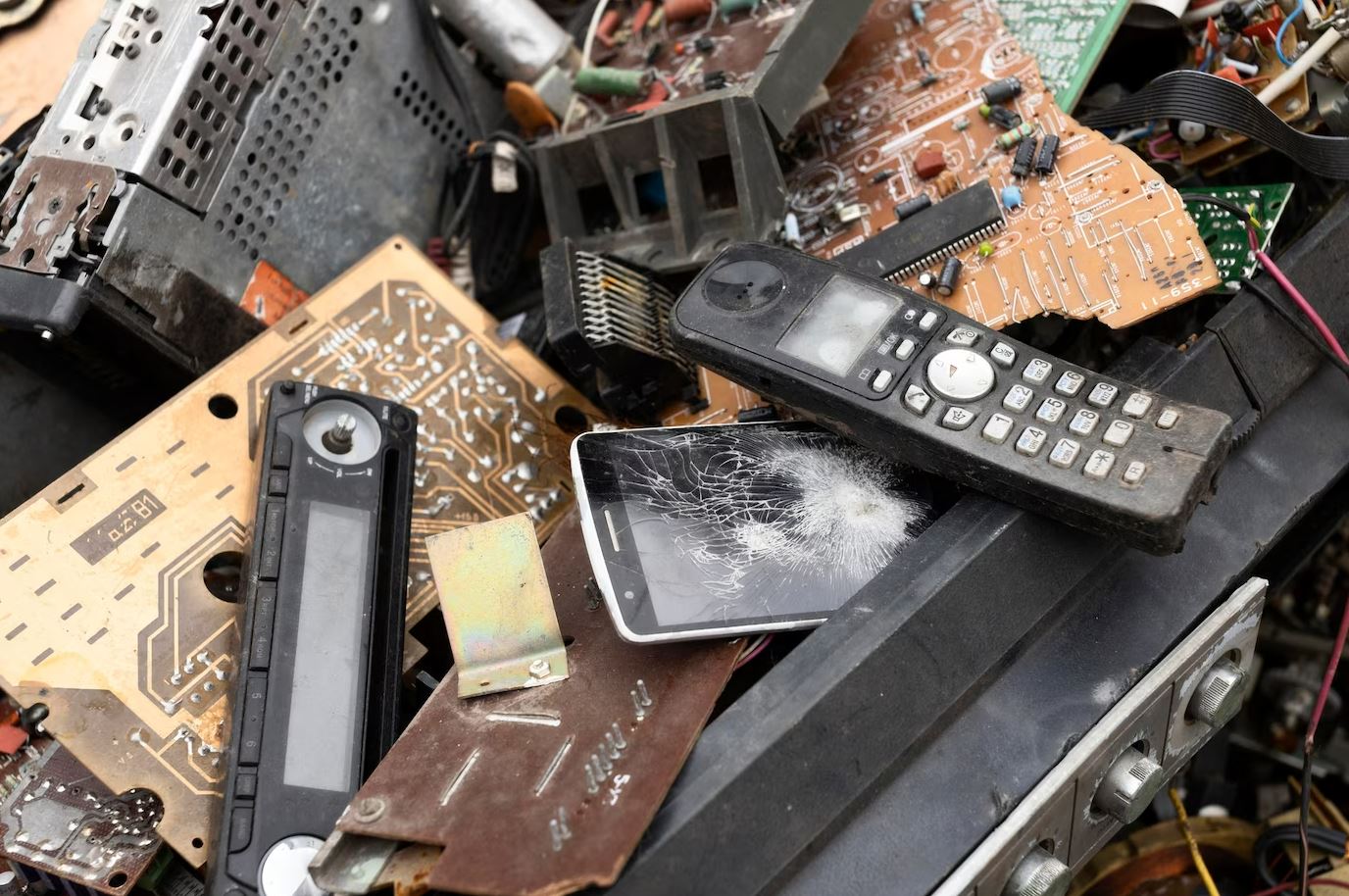

Electronic waste, commonly referred to as e-waste, is a growing concern in our modern society due to the rapid pace of technological advancement and obsolescence. E-waste comprises discarded electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, televisions, refrigerators, and other household appliances, that have reached the end of their useful life or are no longer wanted. These devices often contain valuable materials like metals and plastics, but they also pose significant environmental and health risks if not managed properly.
Electronic Waste Recycling and Management, E-Waste, E-Scrap, Computer Scrap, Waste Electrical and Electronice Equipment (WEEE) Disposal and Managment. All types of Metal, Aluminium, Copper, Brass Stainless Steel Scrap Prices, SS Scraps, SS Scrap, SS Scrap Buyers, Suppliers, Dealers, Traders.
E-waste (electronic waste) management, waste recycling, and the e-recycling process are all crucial aspects of dealing with electronic products and devices at the end of their lifecycle.
E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices and equipment, such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and appliances, that have reached the end of their useful life.
Due to the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing consumption of electronic products, e-waste has become a significant environmental concern.
Environmental Pollution: E-waste contains hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. If not disposed of properly, these chemicals can leach into soil and water, contaminating the environment and posing risks to both wildlife and human populations.
Resource Depletion: Many electronic devices contain valuable materials such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earth metals. Recycling e-waste helps recover these resources, reducing the need for virgin materials and mitigating the environmental impact of mining and extraction.
Data Security: Electronic devices often store sensitive personal or corporate data. Improper disposal can result in data breaches and privacy violations. Therefore, proper data wiping or destruction is crucial before recycling.
Health Hazards: Informal e-waste recycling practices, often prevalent in developing countries, involve burning or dismantling devices without proper safety measures. This exposes workers to toxic fumes and substances, leading to health issues.

E-waste management involves the proper handling, disposal, and recycling of electronic waste to minimize its negative environmental and health impacts. E-waste contains valuable materials like metals, plastics, and glass that can be recovered and reused. However, it also contains hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants, which can pose risks to human health and the environment if not managed correctly.
Recycling is a process of converting waste materials into reusable materials to prevent resource depletion and reduce the environmental impact of waste disposal. In the context of e-waste, recycling involves recovering valuable components from discarded electronic devices to be used in the production of new products. Recycling not only conserves natural resources but also reduces the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with the extraction and processing of raw materials.
Electronic scrap buyers and dealers play a crucial role in the e-waste recycling ecosystem. They purchase electronic waste from various sources, including individuals, businesses, and institutions, and then sell or provide the collected scrap to recycling facilities. These buyers and dealers are often licensed and authorized to handle e-waste and are responsible for ensuring that the waste is properly recycled and disposed of according to regulations.
Computer e-waste recycling specifically focuses on the proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste generated from computers and related equipment. This includes desktop computers, laptops, monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and other computer peripherals. Computer e-waste contains valuable materials like metals and plastics that can be recovered through recycling.
The e-recycling process involves several stages to safely and effectively recover valuable materials from e-waste:

Electronic Waste Computer IT Scrap Recycling - Computer Monitors/Speakers - CRT Monitors, Telephones, Stereo Equipment, LCD Monitors, Cell Phones, Keyboards/Mice, Laptops, Copiers/Printers, Scanners, Televisions, Cameras, Fax Machines, Miscellaneous Wiring, Plasma Screens/TVs, MP3 Players, Items with Electronic Boards, DVD Players, VCRs and Much More!
E-Waste includes all electronic and electrical waste, includes ICT equipment (cellphone, radio, etc.) consumer electronics, small household appliances and large household appliances.
Waste Recycling, e Waste Management, e Recycling - Used Desktop, LED, Laptop & Server Buyer. Authorized Collection, Segregation, Dismantling, Refurbishing and Recycling of E- Waste
E-Waste includes all electronic and electrical waste, includes ICT equipment (cellphone, radio, etc.) consumer electronics, small household appliances and large household appliances.
Computer Motherboard scrap, Press Board Scrap, Ceramic Cpu Processor Scrap, Computer Scrap Buyers, Battery scrap, Ppcp Battery Scrap, Iron scrap, Ac scrap, Motor scrap, Panel Board scrap, Other Products, Panel Board scrap, Mcb scrap, Electronic scrap Buying all scrap products.
Waste Management Services, E Waste Management Services, Solid Waste Management, Garbage Disposal Services, Waste Disposal Service, Electronic Waste Collection Services, Scrap Waste Management, Metal Waste Management, Pharmaceutical E Waste Management, Waste Management Services, Scrap Dealers, Scrap Management, Buying all scrap products.
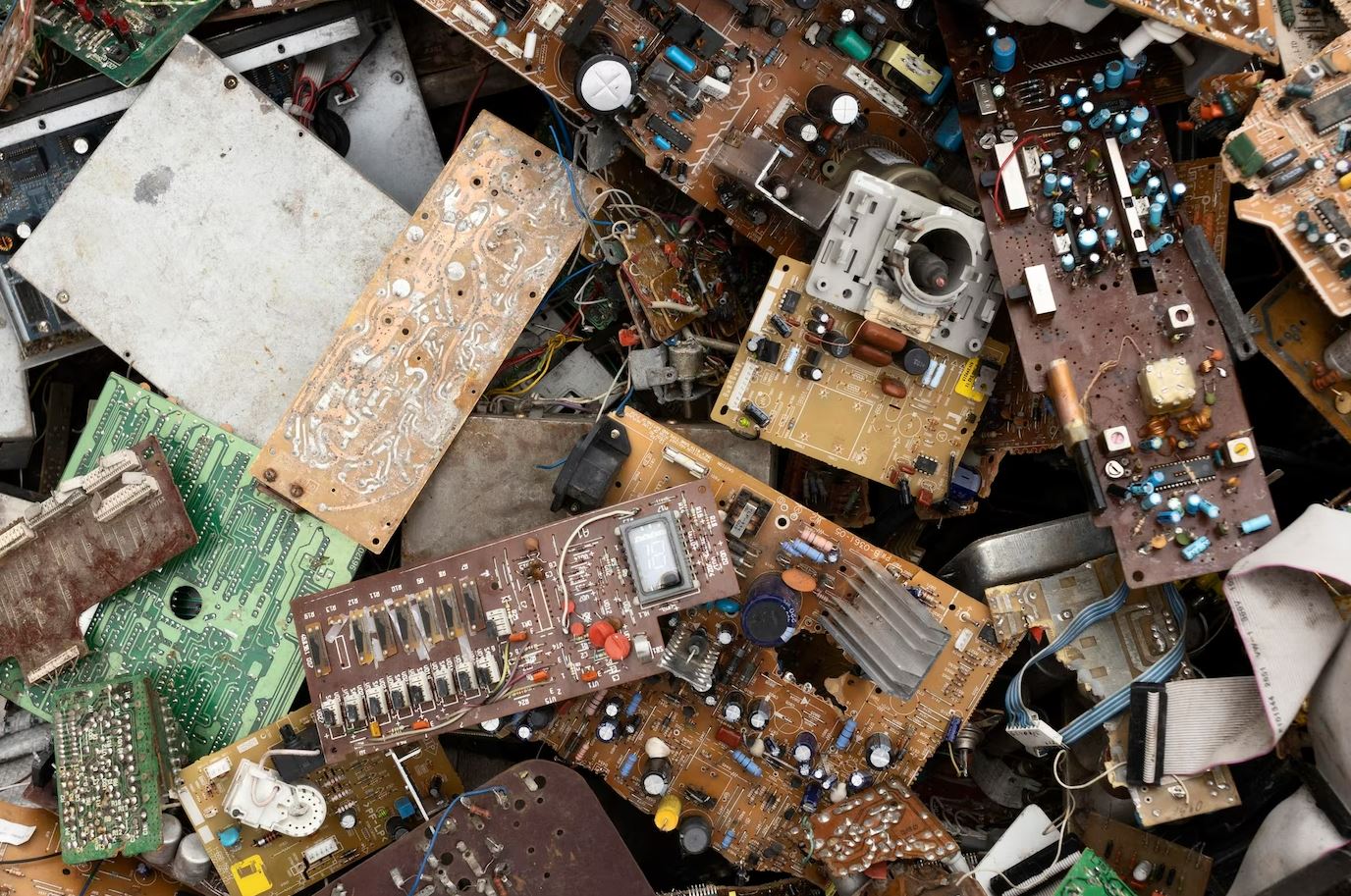

E-Waste includes all electronic and electrical waste, includes ICT equipment (cellphone, radio, etc.) consumer electronics, small household appliances and large household appliances.
Copper Scrap, Aluminium Scrap, MS Scraps, Electronic Scrap, Motor Scrap, Electrical Scrap, Steel Scrap, Brass Scrap, Computer Scrap, Car Scrap, CRC Metal Scrap, Automobile Scrap, CRC Sheet Metal Scrap, AC Scrap, Iron Scrap Buying all scrap products.
Scrap Yard Mumbai is a scrap traders, scrap dealer, scrap purchaser, scrap buyer, scrap merchants mumbai such as Office scrap, Factory Scrap, Household Scrap, Industrial Scrap Iron Scrap, Metal Scrap, Electronic Scrap, Computer Scrap Buyers
Government of India has implemented the "E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016" to regulate the management and disposal of electronic waste. These rules lay down the guidelines and procedures for the environmentally sound management of electronic waste in the country. Here are some key points from the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016:
It's essential to keep up with any updates or amendments to these rules by referring to official government sources, such as the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) in India, or consulting legal professionals familiar with environmental regulations in the country. This information is based on the status as of September 2021, and there might have been changes or updates since then.
Authorized E-Waste Recyclers, Refurbishers, and Dismantlers Disposal Center. E-Waste Recycling, IT Scrap Dealer India
E-waste recycling involves the proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste to minimize environmental pollution and promote the reuse of valuable resources. There are several types of e-waste recycling methods and processes aimed at recovering valuable materials and reducing the negative impacts of electronic waste on the environment. Here are some common types of e-waste recycling:
Leading e Waste recycling company in India offering e Waste management services & recycling solutions
Authorized and licensed companies to ensure proper and environmentally responsible recycling of electronic waste. Authorized companies that are legally permitted to handle e-waste recycling operations.
E Waste Recycling - 100% Recycling Centers in Mumbai Top E-waste Recycling, E-waste Recyclers, Electronic Waste, E-Waste Recycling Company.
Certainly, here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to recycling that might help you understand the concept better:
© 2019 - 2025 Dialup India. All Rights Reserved.
We Accept: 